
Newsletter 2020: Genetic sequencing – the future of medicine is within reach
UK Biobank is enabling a revolution in genetic research – so that we can live healthier lives.
Scientists want to know more about how our genes instruct our cells to behave, how they are influenced by other biochemical signals, and what can be done when they are damaged.
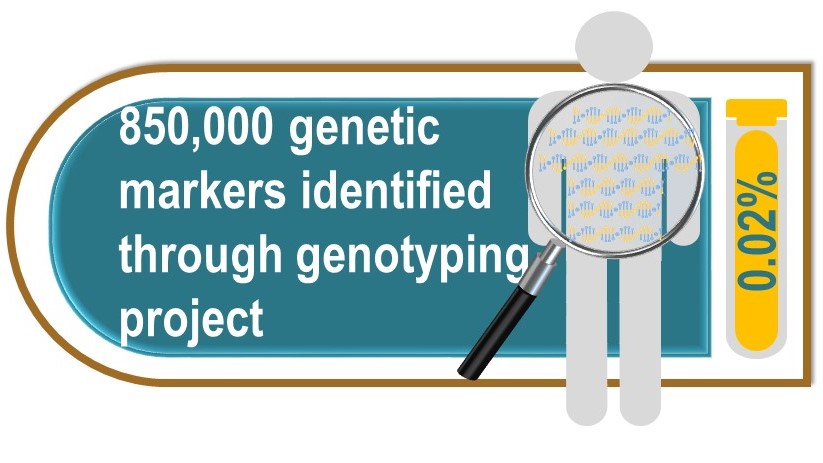
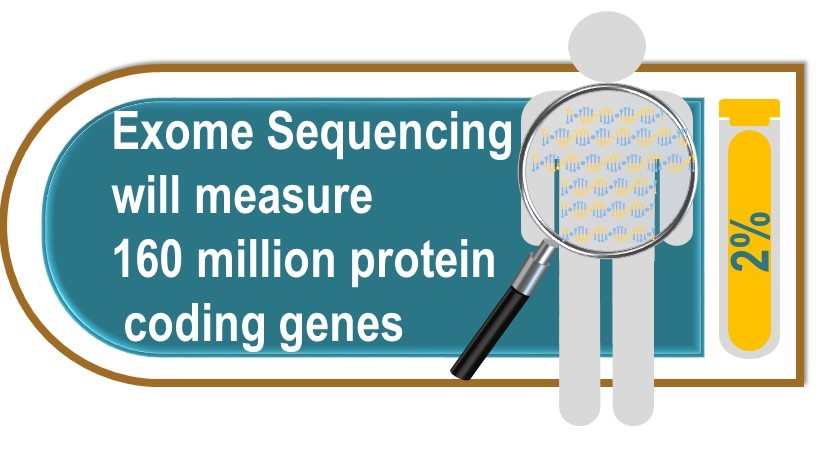
The exome makes up about 2 percent of our genome and contains the protein-coding genes.
Exome sequencing data are particularly valuable for identifying rare genetic variants that affect proteins (and hence bodily function) so can meaningfully lead to the development of new drugs.
UK Biobank has made available exome data for 200,000 participants, which linked to existing detailed genetic and lifestyle data within the database, has created a uniquely rich dataset to gain a greater understanding of human biology and treatments for disease. For example, these data have already shown that many loss of function genes identified in exomes are associated with the human lifespan.
Related news

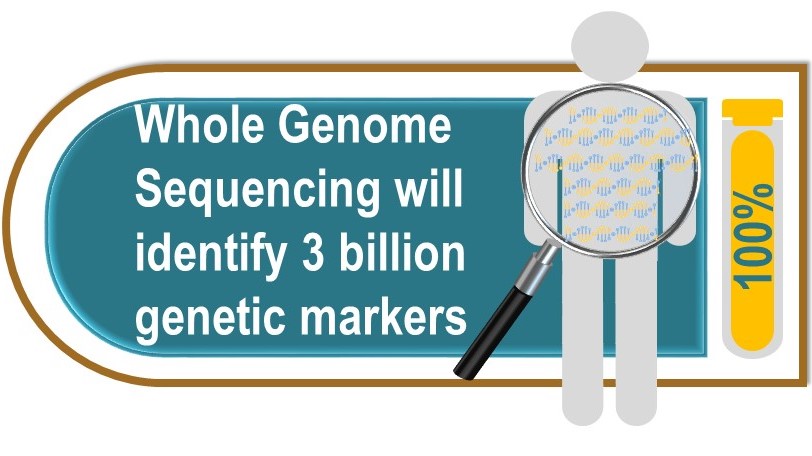
Whole genome sequencing measures all of the letters of the genetic code (of which there are more than 3 billion), in both the coding (exome) and non-coding regions of the genes. These data will provide lots of new information on why some people get particular illness and others do not.
This £200 million project to perform whole genome sequencing on all 500,000 participants was funded by a consortium of Government, charity and industry, comprising of: UK Research and Innovation, The Wellcome Trust, Amgen, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), and Johnson & Johnson (J&J).
The project has set off to a flying start and sequencing of the first 150,000 has already been completed (in addition to the 50,000 that were sequenced through a vanguard project funded by the Medical Research Council). These data will be available to researchers in tranches from next year and will be transformative in developing a better understanding of human biology and treatments for disease.
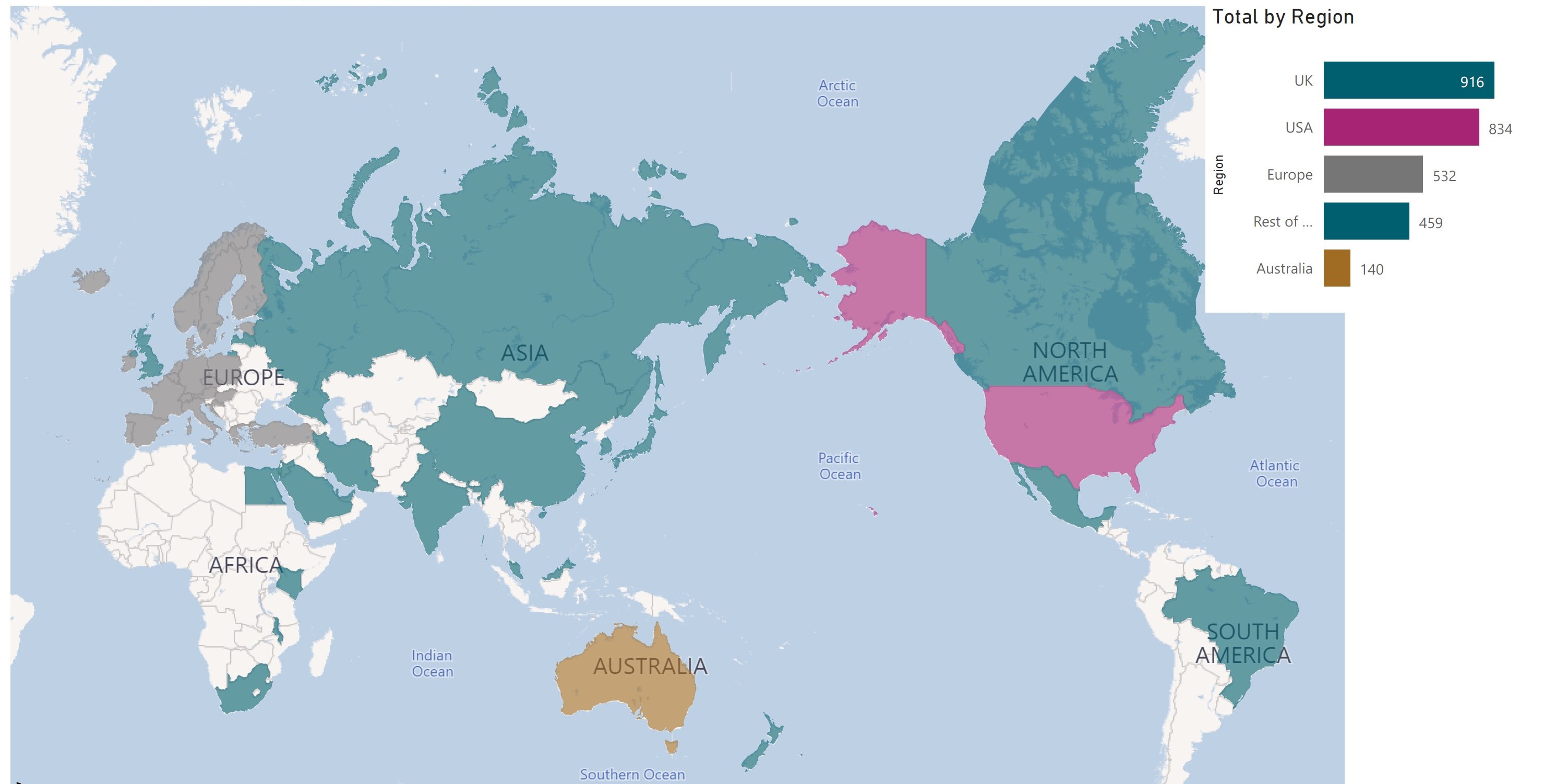
Number of projects approved by country
Last updated
